Understanding how to identify healthy fats is essential for maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet. As fats play a vital role in supporting overall health, being able to distinguish beneficial fats from unhealthy options empowers individuals to make informed dietary choices. This knowledge not only enhances nutritional intake but also contributes to long-term wellness and disease prevention.
Healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, along with omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, offer numerous health benefits. Recognizing these fats involves examining their sources, visual cues, and nutritional labels. By mastering these identification techniques, you can effortlessly incorporate more nutritious fats into your daily meals and improve your overall health.
Introduction to Healthy Fats
In the landscape of nutrition, fats play a vital role in maintaining overall health and supporting bodily functions. While fats have often been associated with weight gain and health risks, it is essential to distinguish between different types of fats to foster a balanced diet. Healthy fats, in particular, contribute significantly to heart health, brain function, and cellular integrity when consumed appropriately.
The importance of including healthy fats in daily nutrition cannot be overstated. These beneficial fats provide essential fatty acids that the body cannot produce independently, such as omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids. Incorporating the right types of fats from natural sources supports immune function, reduces inflammation, and enhances nutrient absorption. Conversely, consuming unhealthy fats, especially trans fats and excessive saturated fats, can lead to adverse health outcomes, including increased cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease.
Types of Fats, Sources, and Effects
Understanding the different categories of fats helps in making informed dietary choices. Below is a comparison table highlighting the main types of fats, their primary sources, and their effects on health:
| Type of Fat | Sources | Effects on Health |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy Fats (Unsaturated Fats) |
|
|
| Unhealthy Fats (Saturated and Trans Fats) |
|
|
Choosing fats wisely involves prioritizing natural, plant-based, and fish sources while limiting intake of processed and fried foods high in trans and saturated fats.
Types of Healthy Fats
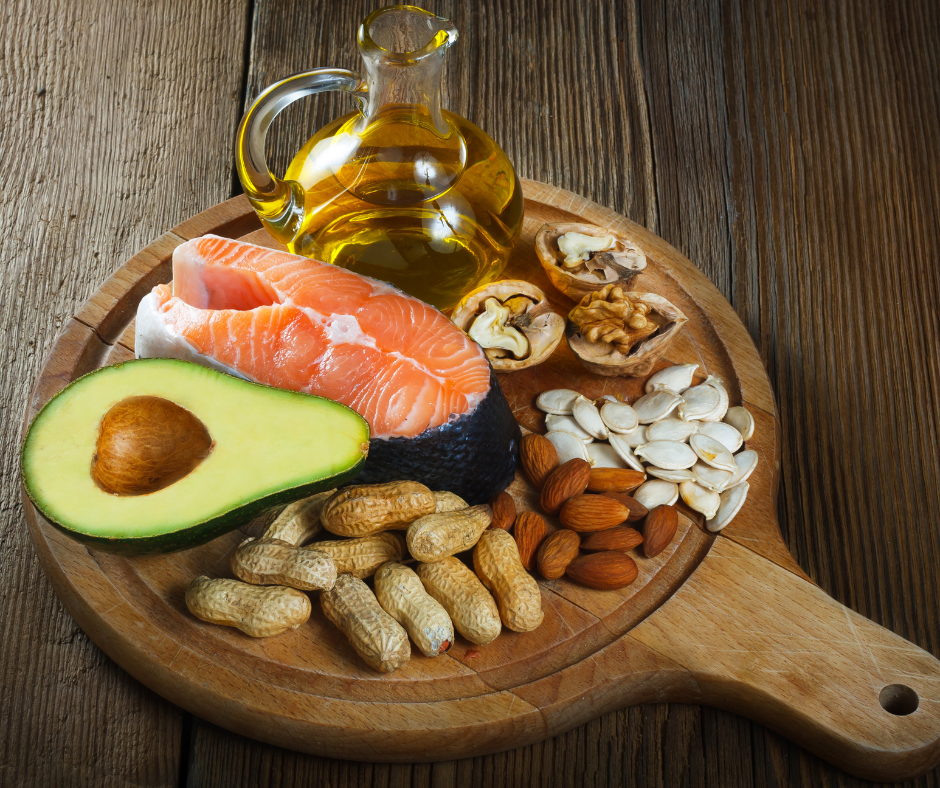

Healthy fats are essential components of a balanced diet, providing vital nutrients that support overall health, including heart function, brain development, and inflammation regulation. Recognizing the different types of healthy fats helps individuals make informed choices to optimize their nutritional intake. Understanding the various categories of healthy fats is important because each type offers unique benefits and is found in specific food sources.
Incorporating a variety of these fats into your diet can contribute to improved cardiovascular health, better hormonal balance, and enhanced cognitive function.
Monounsaturated Fats
Monounsaturated fats are a type of unsaturated fat characterized by having one double bond in their chemical structure. These fats are considered beneficial for cardiovascular health because they help lower bad cholesterol (LDL) levels while increasing good cholesterol (HDL). Consuming foods rich in monounsaturated fats is associated with reduced risk of heart disease and stroke.Food sources rich in monounsaturated fats include:
- Olive oil and extra virgin olive oil
- Avocados
- Nuts such as almonds, cashews, and peanuts
- Seeds like sesame and pumpkin seeds
- Dark chocolate (in moderation)
A diet emphasizing monounsaturated fats can contribute to improved insulin sensitivity and reduced inflammation, making these fats an excellent choice for overall health.
Polyunsaturated Fats
Polyunsaturated fats contain more than one double bond in their molecular structure and are vital for various bodily functions, including cell structure and hormone production. These fats are essential because the body cannot synthesize them; therefore, they must be obtained through diet.Food sources high in polyunsaturated fats include:
- Fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, sardines, and anchovies
- Plant oils like soybean oil, sunflower oil, and corn oil
- Walnuts and flaxseeds
- Safflower oil and sesame oil
Polyunsaturated fats are associated with lowering bad cholesterol levels and reducing inflammation, thus supporting cardiovascular health and brain function.
Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 and Omega-6 fatty acids are specific types of polyunsaturated fats that play crucial roles in maintaining health. Omega-3 fatty acids are renowned for their anti-inflammatory properties, supporting brain health, reducing the risk of heart disease, and aiding in the management of inflammatory conditions. Sources include fatty fish, flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.Omega-6 fatty acids, on the other hand, are primarily involved in promoting growth and development, as well as regulating metabolism.
They are found in vegetable oils such as corn oil, soybean oil, and sunflower oil. While essential, maintaining a balanced intake of Omega-6 to Omega-3 is important because an excess of Omega-6 can promote inflammation.Sources of Omega-3 fatty acids:
- Fatty fish like salmon and sardines
- Chia seeds and flaxseeds
- Walnuts
Sources of Omega-6 fatty acids:
- Vegetable oils such as sunflower, corn, and soybean oil
- Nuts and seeds
Proper intake of these essential fatty acids supports optimal brain function, reduces inflammation, and contributes to overall cardiovascular health.
Fats Category Table

| Type | Source | Benefits | Recommended Intake |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monounsaturated Fats | Olive oil, avocados, nuts, seeds, dark chocolate | Lower LDL cholesterol, improve insulin sensitivity, reduce inflammation | Replace saturated fats with monounsaturated fats; about 15-20% of daily calories |
| Polyunsaturated Fats | Fatty fish, vegetable oils, walnuts, flaxseeds | Support cell function, lower bad cholesterol, reduce inflammation | Include in meals regularly; balance Omega-3 and Omega-6 intake |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Fatty fish, flaxseeds, walnuts | Reduce inflammation, support brain and heart health | At least two servings of fatty fish per week or 250-500 mg daily from supplements or food sources |
| Omega-6 Fatty Acids | Vegetable oils, nuts, seeds | Promote growth, regulate metabolism, support immune function | Keep balanced with Omega-3 intake; typically higher in Western diets |
How to Recognize Healthy Fats in Foods
Identifying healthy fats in foods is essential for maintaining a balanced diet and promoting overall health. While many foods naturally contain beneficial fats, recognizing their presence requires an understanding of visual cues, ingredient labels, and nutritional information. This awareness empowers you to make smarter food choices and incorporate healthy fats effectively into your daily meals.
By learning to read food labels and understanding the common sources of healthy fats, you can easily distinguish nutrient-rich options from those containing less desirable fats. Incorporating a variety of natural, whole foods high in healthy fats supports cardiovascular health, brain function, and overall well-being.
Visual Cues and Ingredient List Indicators of Healthy Fats
When examining food packaging or choosing foods at the grocery store, certain visual cues and ingredient indicators can help identify healthy fats. These cues include specific labels, ingredient mentions, and the nature of the product itself.
- Labels and Claims: Look for terms such as “rich in omega-3,” “contains healthy fats,” or “heart-healthy.” Products labeled as “unsaturated fats” or “sources of omega-3” are good indicators.
- Ingredient List: Focus on foods with ingredients like nuts, seeds, fish oils, olive oil, or avocado. The presence of these indicates natural sources of healthy fats.
- Color and Texture: In whole foods, vibrant colors and firm textures often signify freshness and nutrient density, which can correlate with healthy fats, especially in nuts, seeds, and oily fish.
Common Foods Rich in Healthy Fats with Descriptive Attributes
Many foods naturally contain beneficial healthy fats that support optimal health. Recognizing these foods by their characteristics can help you incorporate them into your diet effortlessly.
Foods high in healthy fats typically have rich, oily textures and may be nutrient-dense or have distinct flavors indicative of their fat content.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, and flaxseeds are packed with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, offering a crunchy texture and nutty flavor.
- Fatty Fish: Salmon, mackerel, sardines, and trout are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids, characterized by their oily, moist flesh and distinctive aroma.
- Plant Oils: Extra virgin olive oil, avocado oil, and flaxseed oil are liquid at room temperature with a smooth consistency and rich aroma, indicating nutrient richness.
- Avocados: Known for their creamy texture and vibrant green color, avocados are high in monounsaturated fats and fiber.
Reading Nutrition Labels to Identify Healthy Fat Content
Nutrition labels provide vital information that can help you determine the quality of fats present in packaged foods. It’s important to interpret these labels accurately to make healthier choices.
- Check the Total Fat Section: Look for foods where the total fat content is primarily composed of unsaturated fats. A lower saturated fat amount is preferable.
- Identify Types of Fat: Examine the breakdown of fats—monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats should be listed separately. Higher percentages of these fats indicate healthier options.
- Note the Trans Fats: Aim for foods containing zero trans fats, as these are artificially hydrogenated fats associated with adverse health effects.
- Review Omega-3 and Omega-6 Content: Some labels specify these essential fatty acids. Look for products enriched or naturally high in omega-3s, such as fish oils or flaxseed addition.
Understanding how to interpret nutrition labels empowers you to prioritize foods with beneficial healthy fats, contributing to a balanced and nutritious diet that promotes long-term health benefits.
Methods for Incorporating Healthy Fats into Diet

Integrating healthy fats into your daily meals is an essential step toward achieving a balanced and nutritious diet. Proper incorporation not only enhances flavor and satisfaction but also supports overall health, including heart health, brain function, and inflammation reduction. Developing practical strategies to include these fats consistently can lead to sustainable dietary habits that promote well-being.
By focusing on simple, mindful methods, individuals can effortlessly add healthy fats to their meals. This involves selecting nutrient-rich ingredients, preparing foods with healthy fats, and balancing intake according to dietary guidelines. The following sections Artikel effective ways to incorporate healthy fats into everyday eating patterns, provide step-by-step preparation tips, organize meal ideas with relevant ingredients, and share helpful tips to maintain optimal fat intake levels.
Including Healthy Fats in Daily Meals
To effectively incorporate healthy fats into your diet, consider these practical approaches:
- Use oils such as extra virgin olive oil, avocado oil, or flaxseed oil for cooking, salad dressings, or drizzling over dishes.
- Add sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, and seeds to salads, sandwiches, and snacks.
- Include fatty fish such as salmon, mackerel, or sardines in your weekly meal plan to boost omega-3 intake.
- Use nut butters or tahini as spreads or ingredients in smoothies and sauces.
- Replace saturated fats with healthy fats in recipes, for example, using mashed avocado instead of butter in baking or spreads.
These methods ensure that healthy fats are seamlessly integrated into meals, enhancing both nutritional value and taste.
Step-by-Step Procedures for Preparing Foods High in Healthy Fats
Preparing foods rich in healthy fats involves selecting quality ingredients and employing cooking techniques that preserve their beneficial properties. The following steps provide guidance for preparing such foods:
- Select fresh, high-quality ingredients: Choose fresh fish, nuts, seeds, and oils to maximize nutrient content.
- Prepare ingredients: For fatty fish, season with herbs and lemon, then bake or grill at moderate temperatures to retain omega-3s. Wash and chop vegetables and fruits to add healthy fats.
- Use appropriate cooking methods: Opt for baking, steaming, or grilling instead of deep-frying to avoid unnecessary trans fats and excess calories.
- Incorporate healthy fats into dishes: For salads, use extra virgin olive oil and vinegar. In smoothies, blend with nuts or seeds for added fats and nutrients.
- Store prepared foods properly: Keep oils in airtight containers away from heat and light to prevent oxidation and rancidity.
This systematic approach ensures that healthy fats are preserved during preparation and incorporated effectively into meals.
Meal Ideas, Ingredients, and Healthy Fats Involved
Below is a table illustrating various meal ideas that incorporate healthy fats, along with their key ingredients and the type of healthy fat involved:
| Meal Idea | Ingredients | Healthy Fats Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Avocado Toast | Whole grain bread, ripe avocado, olive oil, lemon juice, sea salt, pepper | Monounsaturated fats from avocado and olive oil |
| Grilled Salmon Salad | Salmon fillet, mixed greens, cherry tomatoes, cucumbers, extra virgin olive oil, balsamic vinegar | Omega-3 fatty acids from salmon, monounsaturated fats from olive oil |
| Nuts and Seeds Snack | Mixed almonds, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds | Polyunsaturated fats, omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids |
| Homemade Nut Butter | Raw almonds or cashews, a pinch of sea salt, optional honey | Monounsaturated fats |
| Yogurt with Chia Seeds and Berries | Greek yogurt, chia seeds, mixed berries, a drizzle of honey | Healthy fats from chia seeds, probiotics from yogurt |
Each of these meals emphasizes healthy fats as integral components, enriching flavor and nutritional value.
Tips for Balancing Fat Intake within Dietary Guidelines
To maintain a healthy balance of fats in accordance with dietary recommendations, consider these tips:
- Limit saturated fat intake by reducing consumption of processed foods, fried items, and high-fat dairy products.
- Prioritize sources of unsaturated fats, such as olive oil, avocados, nuts, and fatty fish.
- Monitor portion sizes to avoid excessive calorie intake from fats, as they are calorie-dense.
- Incorporate a variety of fat sources to ensure a balanced intake of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids.
- Read nutrition labels carefully to identify trans fats and limit their consumption.
- Follow recommended guidelines, such as consuming fats constituting about 20-35% of daily calories, with the majority from unsaturated sources.
Remember that moderation is key; incorporating healthy fats thoughtfully supports overall health without exceeding recommended intake levels.
Myths and Misconceptions about Healthy Fats
Understanding the truth about dietary fats is essential for making informed nutritional choices. Despite extensive research, several myths persist that can lead to confusion and misguided eating habits. Clarifying these misconceptions helps individuals focus on consuming healthy fats responsibly and effectively.
Many common beliefs about fats stem from outdated information or oversimplifications, often leading to unnecessary fear or overconsumption of certain food groups. Debunking these myths allows for a balanced approach, emphasizing moderation and quality in fat intake. Recognizing what is factually accurate supports healthier dietary patterns and reduces misconceptions that may hinder overall well-being.
Common Myths and Facts about Healthy Fats
Here are some widespread myths about fats, along with factual clarifications to help dispel confusion:
- Myth: All fats are harmful and should be avoided.
- Fact: Not all fats are detrimental; healthy fats such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats are beneficial for heart health and overall wellness. The key lies in choosing the right types and consuming them in moderation.
- Myth: Eating fats causes weight gain regardless of the quantity.
- Fact: Excessive calorie intake from any macronutrient can lead to weight gain. Healthy fats are calorie-dense, but when incorporated thoughtfully into a balanced diet, they can aid in satiety and weight management.
- Myth: Low-fat or fat-free foods are always healthier choices.
- Fact: Removing fats from foods can sometimes increase sugar and additive content to preserve flavor, which may be less healthy. It is better to select whole, minimally processed foods with natural healthy fats.
Importance of Moderation and Quality in Fat Consumption
While healthy fats are beneficial, consuming them in moderation is vital to avoid unintended health issues. Overconsumption, even of good fats, can contribute to calorie overload and metabolic imbalance. Emphasizing the importance of quality involves selecting fats from reputable sources, such as extra virgin olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds, which are minimally processed and rich in nutrients.
“The quality of fats matters just as much as the quantity. Prioritize natural, unrefined sources of healthy fats for optimal health.”
Implementing a balanced approach—focusing on the type, source, and quantity of fats—ensures that the dietary benefits of healthy fats are maximized while minimizing potential drawbacks. Educating oneself about these truths fosters smarter food choices and supports long-term health goals.
Benefits of Consuming Healthy Fats
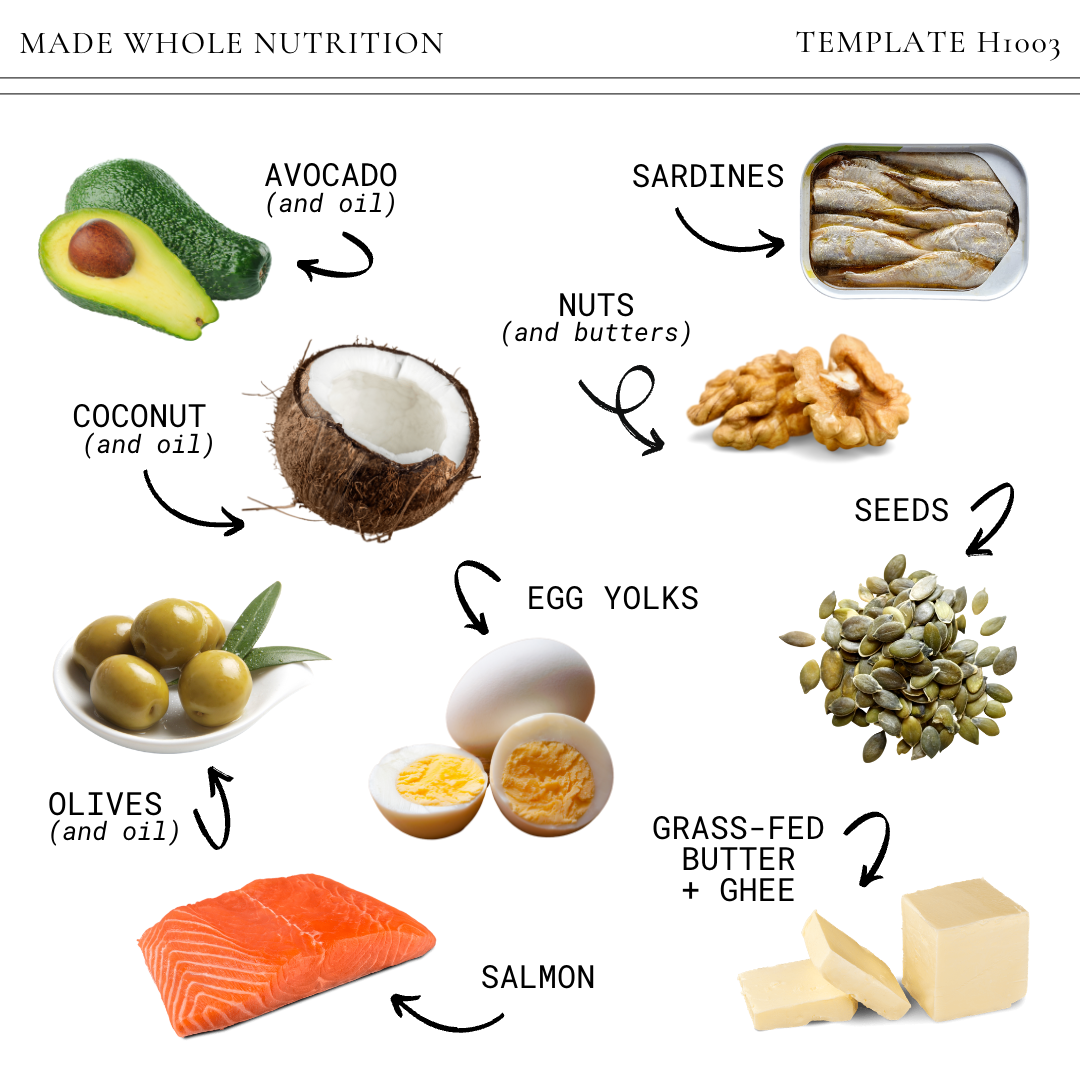
Incorporating healthy fats into your diet offers numerous advantages that contribute to overall wellness. These fats are essential not only for maintaining bodily functions but also for enhancing long-term health outcomes. Understanding the specific benefits can motivate consistent dietary choices that favor healthier fat sources.
Healthy fats play a vital role in supporting cardiovascular health, brain function, and reducing inflammation within the body. Their positive effects extend beyond immediate well-being, contributing to the prevention of chronic diseases and fostering a more resilient physiological state.
Cardiovascular Health
Healthy fats, particularly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, have been shown to improve heart health by lowering bad cholesterol (LDL) levels and increasing good cholesterol (HDL). These fats help reduce the risk of atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries. For example, Omega-3 fatty acids found in fatty fish like salmon and mackerel have been linked to a decreased incidence of heart attacks and strokes.
Regular consumption of these fats supports a healthier cardiovascular system over the long term.
Brain Function and Cognitive Performance
Fats are essential components of brain tissue, and healthy fats are particularly crucial for cognitive processes. Omega-3 fatty acids, such as EPA and DHA, contribute to improved memory, concentration, and mental clarity. They also play a fundamental role in neurodevelopment and are associated with a lower risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s. Consuming adequate healthy fats can enhance mood regulation and mental resilience, especially in aging populations.
Reduction of Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is linked to many health conditions, including arthritis, diabetes, and heart disease. Healthy fats, especially omega-3 fatty acids, have anti-inflammatory properties that help mitigate this response. They modulate the production of inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins, leading to a reduction in inflammation markers within the body. This benefit is particularly significant for individuals with autoimmune conditions or those at risk of inflammatory-related illnesses.
Long-term Health Improvements
Consistent intake of healthy fats has been correlated with numerous long-term health benefits. These include a lower risk of developing metabolic syndrome, improved lipid profiles, and better weight management. For instance, populations that consume diets rich in healthy fats, such as the Mediterranean diet, tend to experience lower rates of cardiovascular disease and better overall longevity. Additionally, healthy fats support hormone production, immune function, and cell integrity, all of which are integral to maintaining comprehensive health over the years.
Healthy fats are fundamentally important for nurturing a balanced, vibrant, and resilient body. Their role in supporting vital functions and preventing disease underscores the importance of choosing quality fat sources as part of a well-rounded diet.
Closing Summary

In conclusion, accurately identifying healthy fats is a crucial step toward optimizing your diet for better health outcomes. By focusing on natural sources, reading labels carefully, and understanding the benefits of these beneficial fats, you can enjoy a more balanced and nourishing lifestyle. Embracing healthy fats ensures your body receives the support it needs for optimal function and long-term vitality.